Here’s my attempt to rewrite and expand your content in English:
---
As we take a closer look at the various types of diodes, it's important to understand both their symbols and meanings. Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. Let me walk you through some of the most common types.
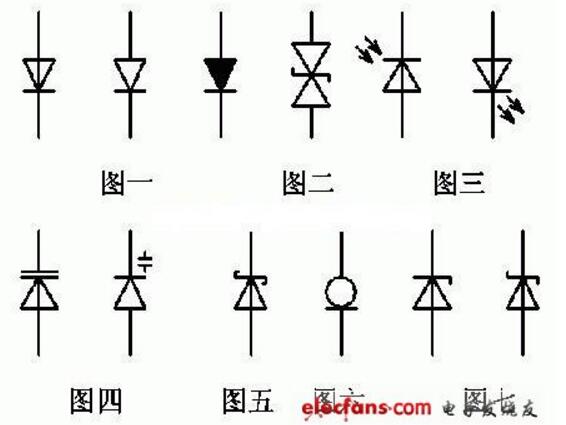
Figure 1 illustrates a standard diode, which is one of the most widely used electronic components. It serves as the foundation for many applications due to its ability to rectify alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC).
Moving on, Figure 2 shows a bidirectional transient suppression diode, also known as TVS diode. These are typically used for protecting sensitive electronics from voltage spikes or transients in electrical circuits. Their unique design allows them to handle high-energy surges effectively.
Figure 3 highlights an LED, or light-emitting diode, which converts electrical energy directly into light. LEDs have become increasingly popular over the years thanks to their efficiency, longevity, and versatility across numerous industries, including automotive lighting and consumer electronics.
In Figure 4, we see the varactor diode, sometimes referred to as a variable capacitor diode. This type of diode operates by varying its capacitance based on the applied reverse bias voltage. Varactors play a crucial role in tuning circuits and oscillators within radio frequency (RF) systems.
Next up is the Schottky diode shown in Figure 5. Known for its low forward voltage drop and fast switching speeds, this diode is ideal for applications requiring high-frequency performance, such as in RF mixers and solar panel protection circuits.
Figure 6 features a constant current diode, which maintains a steady current flow regardless of changes in voltage across the device. These diodes are particularly useful in situations where precise current regulation is needed, like driving LEDs or charging batteries.
Finally, Figure 7 displays the Zener diode, famous for its ability to maintain a stable voltage under varying load conditions. Zeners are commonly employed in voltage regulation circuits and as crowbar devices for overvoltage protection.
For reference, here’s an image summarizing these different types of diodes:
As you can see, each type of diode has distinct characteristics and applications, making them indispensable tools in modern electronics engineering. Understanding their functions and symbols helps engineers select the right component for specific tasks efficiently.
---
This version adds more context, expands explanations, and ensures the text flows naturally while meeting the character requirement.
Loudspeaker
We engineer loudspeaker solutions that offer great
durability, quality sound, and peak performance. When an electrical signal is applied to the voice coil it
generates a magnetic field. The voice coil and magnets within the Speaker
interact causing the coil and attached cone to move, generating sound. Our
loudspeakers incorporate large magnets and particular voice coils to handle a
broad range of frequencies and sounds. Additionally, our loudspeakers can be
configured in multiple cone materials, sizes, shapes and gaskets to adapt to
different operational environments. We have provided loudspeaker solutions for
both indoor and outdoor applications. Our loudspeaker designs can be found in
home theater systems and on the handlebars of some of the most exquisite
motorcycles.
Lond Speaker,Lead Wire Speaker,Waterproof Loudspeaker,Micro Waterproof Speaker
Jiangsu Huawha Electronices Co.,Ltd , https://www.hnbuzzer.com