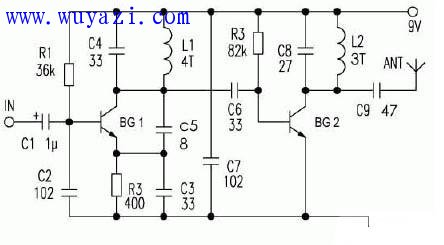
3KM meter wireless FM transmission circuit diagram
The circuit operates at a voltage of 9V with a current range of 2–6mA. The component details are illustrated in the diagram. BG1 is a 9018 transistor, and BG2 is a C1959 (which can also be replaced with a 9018, though it has lower power). If you use a D-40 transistor, the transmission distance can be extended up to 1000 meters. However, D-40 might be harder to find in local electronics stores.
The coils L1 and L2 are wound with 0.5mm enameled wire around a 0.5mm diameter rod, with 4 turns for L1 and 3 turns for L2. By increasing the working voltage to 12V, the transmission distance can be further extended. However, this may cause a slight change in frequency. For optimal performance, it's recommended to power the entire circuit using batteries, which helps maintain better sound quality and frequency stability.
During the debugging process, start by turning off BG2. Adjust the desired frequency first, then turn on BG2 and fine-tune the power. In my setup, I used BG1 as a D-40 and BG2 as a C1970, which worked very well at 12V. BG1 was operated at 6V, and the transmission distance reached 3000 meters in a directional test.
If you plan to use a D-40 transistor, make sure its operating voltage is 6V. It's also advisable to install the circuit inside an iron box with a damping network at the input to reduce interference and improve signal quality.
Others
Others
HuiZhou Antenk Electronics Co., LTD , https://www.atkconn.com