Design of Vehicle Energy Measurement System Based on New Components of LEM
With the development of technology, energy demand is getting bigger and bigger. With the exhaustion of energy, energy consumption has become more and more important in many fields, and the railway industry is no exception. By monitoring the energy and cost list of each train, it can motivate railway operators to optimize energy use efficiency. This article describes the new components of LEM; this is the first system to meet the latest interim standard EN50463 for energy monitoring and cost accounting.
This article refers to the address: http://
Automotive energy-saving technologies are used to improve the energy consumption of automobiles. Automobile energy-saving measures cover all aspects. As far as China's current situation is concerned, effective measures include the following aspects: reasonable matching of roads and transportation facilities, production and configuration of vehicles and oils on demand, and reasonable operation and other non-technical issues. In terms of technology, the product quality is guaranteed, the machine is used and maintained according to the specifications, and the combustion mode of the gasoline engine is changed to improve the energy conversion efficiency.
In the existing combustion mode, energy saving can be adopted by: improving the fuel supply system, changing the fuel injection of the gasoline engine to improve the combustion efficiency of the gasoline; improving the ignition system, improving the running stability of the gasoline engine; reducing the loss of engine accessories, and rationally using the accessories , carry out the corresponding modification.
In many cities, for the sake of beauty and style, the main blocks of the office buildings are glass curtain walls, and many large dome buildings have been built as public facilities. In the summer, ultraviolet radiation is intense, causing light pollution. In winter, it does not block the cold. In the whole year, high-power air conditioners must be opened to regulate the temperature. In winter, other buildings should be kept warm, and in the summer, other buildings should be cooled.
According to incomplete statistics, the existing glass curtain wall (non-energy-saving glass) area in the country has exceeded 9 million square meters, and it is in a continuous development trend. The glass curtain wall brings about a so-called aesthetic, but also brings about a doubling of energy consumption.
Almost every area of ​​our lives is under pressure to reduce CO2 emissions from energy consumption to mitigate environmental damage. Although the railway industry produces less carbon dioxide emissions than other modes of transportation, there is still a need to further improve energy efficiency.
According to a recent study by the UK Department of Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, the amount of CO2 produced per kilometer per passenger by rail is only 61g, while the amount of CO2 produced per kilometer per passenger is as high as 140g (the average vehicle emissions are based on an average of 1.5). ).
For rail operators that actually consume energy, one way is to monitor and set targets to reduce energy consumption, costs, and emissions. If drivers are encouraged to avoid energy waste – that is, “energy-saving drivingâ€, it is especially important to provide detailed driving information for each trip.
In the future, drivers may use the recommended optimal energy-saving speed. It combines with the new concept of how to drive more economically, and can save more than 10-20%.
For fossil fuel engines, fuel consumption measurements are relatively simple, but in an electrified line accurate traction energy measurement system, the cost of distribution and the carbon impact of each trip are necessary for the operator. If this is to be achieved, then every train needs an effective on-board energy measurement method.
The system must record energy consumption and location, enabling operators to grasp the reasons for higher energy consumption and provide a list of fees for different grid operators. The interim standard EN50463 has been developed, which meets all possible requirements related to train energy measurement.
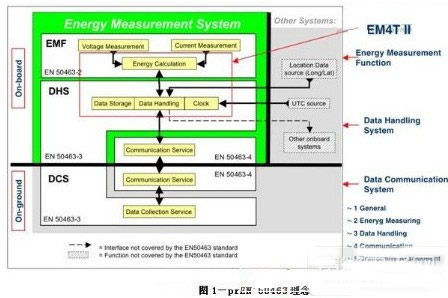
If the standards are well established, they will be implemented successfully. The development of prEN50463 takes into account the opinions of many different stakeholders, from railway operators to equipment manufacturers, in addition to the TSI basic requirements specification and UIC recommendations.
The standard is divided into 5 parts:
- prEN 50463-1: Scope, general architecture, file structure, standard references, general requirements
——prEN 50463-2: Voltage/current sensor measurement chain from OCL to metering unit
--prEN 50463-3: All input/output data processing and memory management units
——prEN 50463-4: Vehicle and “train-ground†communication system
——prEN 50463-5: Test procedure specification used to assess the consistency and synergy of the system under test
The three main functional blocks of the Energy Measurement System (EMS) are described in Sections 2-4. They require all traction systems to be processed for the intended operation of the train. The core of the system is the Energy Measurement Function (EMF) described in Part 2, which measures current and voltage and calculates energy consumption. The EMF consists of 3 parts:
- Current Measurement Function (CMF)
- Voltage Measurement Function (VMF)
- Energy Calculation Function (ECF)
In railway applications, current and voltage measurements and energy calculations face a major engineering challenge. Driving modern trains consumes a lot of power. Standard multi-standard freight trains exceed 6.4 MW. EMS must meet the accuracy standards. The standard that may eventually be adopted is 0.5 R (each component is accurate to 0.5R1).
The railway sector also faces environmental challenges: any EMF must be able to cope with wide operating temperatures and strong mechanical stresses. The system must be able to prevent dust and water from entering - some operators require the enclosure to reach IP65. Temperature fluctuations can be large and designers must consider the possibility of condensation.
At such high supply voltages, the key challenge for VMF is to ensure adequate isolation. The sensor exhibits good common mode performance - measuring the actual voltage difference between the two conductors and ignoring any common ground voltage offset.
The development of CMF is also very challenging because the high current measurement accuracy is difficult to reach 0.5R. The most commonly used current sensor technology - the Hall effect - does not achieve the required accuracy. Using a shunt may be a simple alternative to measuring the voltage drop across a small resistor so that the current can be calculated by Ohm's law. However, this method has inherent drawbacks, and the power consumed by the shunt can cause heat dissipation problems.
A CMF sensor developed by LEM meets the accuracy requirements of 0.5R. The difficulty of developing a CMF that satisfies the 0.5R accuracy illustrates the fact that the ITC 4000 is currently the only sensor with an accuracy that can reach this specification.
ECF is a complex feature. In the railway sector, electrical energy calculations are more complex than the simple multiplications of the voltages and currents we have learned at school. Therefore prEN 50463 requires EMF to calculate reactive and active (actual) power.
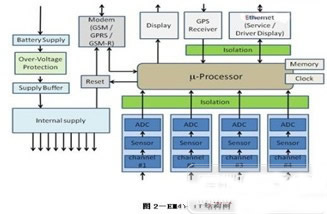
Figure 2 shows a good example of how the LEM EM4T II (Traction Energy Meter II) implements EMF. The EM4T II takes readings from the CMF and VMF and can also be connected to a GPS device to allow plotting with a position data load curve. The GPS interface also provides a highly accurate clock signal for time stamping load information.
Data can be read from the EM4T II using the serial interface. The data is extracted from the data processing system within the EM4T II and transmitted to the terrestrial system via the communication network. The EM4T II can be configured with a second interface to ensure that the system meets the specific requirements of any rail operator.
This paper proposes that on-board energy measurement and reporting requires a complex system that not only calculates energy, but also records position, time-stamp data and then transmits the information to the ground system. Although the standard has not been fully approved, VMF and CMF components that meet the challenging specifications of 0.5R have been introduced. Combining them with ECF components, it is possible to develop an in-vehicle EMS that meets the requirements of prEN 50463 using other off-the-shelf GPS and communications products.
Commercial Coffee Urn,Coffee Urn,100 Cup Coffee Urn,Large Coffee Urn
FOSHAN FORTUNE ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE CO.,LTD , https://www.coffelady.com