Why is LPWA a disruptive new network for the Internet of Things?
If you are constantly concerned about the Internet of Things, in the IoT space, you will not miss the emergence of a new class of IoT network operators that are competing to provide low-power wide-area (LPWA) coverage for applications. The French company Sigfox is one of the most eye-catching of these LPWA network technology companies, as its supporters include Orange and Telefonica. But there are many other LPWA companies, including LoRa, Qowisio, Nwave, Ingenu, Telenasa and Rajant. There is even a special association on this, the Wireless IoT Forum.
The rise of “LPWA†has benefited from the rapid development of the Internet of Things in recent years. As we all know, the foundation of the Internet of Everything is to use communication technology to connect people and things, things and things. Our familiar communication technologies include short-range wireless communication technologies such as WIFI, Bluetooth, ZigBee, and mobile cellular such as 2G, 3G, 4G/LTE. Communication technology (wireless communication technologies such as industrial bus, Ethernet, and optical fiber are not discussed here).
Ovum chief research officer Mark Newman said that the rapid rise of this type of company is very interesting on many levels. First, it represents a challenge to mobile operators that dominate part of the value chain, which refers to the part of the carrier that they believe they can generate revenue through existing network assets. Second, the wave of LPWA technology and operators is at a time when the global mobile industry is in the process of inducing 5G technology into the IoT market. Third, LPWA's wireless capabilities and low cost mean that it will be possible to extend coverage to areas that cannot be covered by current cellular networks.
Why does LPWA appear?
Short-range communication technology is generally used in LAN communication scenarios such as smart home and industrial data acquisition. Its advantages are low deployment cost, low power consumption, and high transmission rate, but the disadvantages are also obvious - short transmission distance (generally within tens of meters) ). With the increase of networked devices, the types of devices and application scenarios, more and more devices require wide-ranging and long-distance connections, such as remote control and logistics tracking. You will ask, is there not mobile cellular communication technology?
Indeed, the global telecom operators have built a global mobile cellular network, and our proud Huawei company has already had mobile phone signals on the Himalayas. Moreover, in addition to the main mobile cellular network to meet the call, texting, and friend circle (access to the Internet), more and more mobile Internet services are beginning to carry Internet of Things applications such as remote meter reading and car networking. However, cellular networks such as 2G, 3G, and 4G have wide coverage, but IoT devices based on mobile cellular communication technologies have disadvantages such as high power consumption and high cost. The mobile cellular communication technology was originally designed for human-to-human communication. According to an authoritative analysis report, the current global connection of objects and objects actually carried on the mobile cellular network accounts for only 6% of the total number of connections. The main reason for such a low proportion is that the current mobile cellular network has insufficient carrying capacity to support the connection of objects.
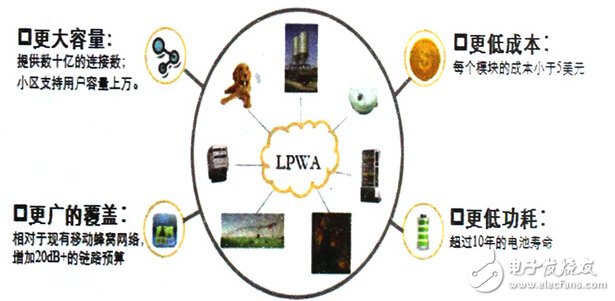
Therefore, in order to meet the connection needs of more and more long-distance IoT devices, LPWA came into being. LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network), a low-power wide-area network designed for low-bandwidth, low-power, long-distance, and massively connected IoT applications. Just as short-range wireless networks include WIFI, Bluetooth, ZigBee and many other technologies, LPWA also includes a variety of technologies, such as LoRa, Sigfox, Weightles and NB-IoT. Because it is a "wide area" network, it will inevitably involve network operations. Therefore, the LPWA network is generally deployed by a telecom operator or a specialized IoT operator. Since the LPWA network connection is basically a "thing", it is usually called an "Internet of Things-only network."
Why choose LPWA?
LPWA has three characteristics of "long-distance communication", "low-rate data transmission" and "low power consumption", so it is very suitable for IoT applications with long-distance transmission, small amount of communication data, and long-term operation with battery power. Most IoT applications usually only need to transfer a small amount of data, such as sensors that control switches in industrial production plants. Data is generated only when the switch is abnormal. These devices generally consume a small amount of power and can be powered by batteries. Work for a long time.
LPWA is best suited for two types of IoT applications: one is a fixed-location, relatively densely-concentrated scenario, such as smart water meters, warehouse management, or other device data acquisition systems in buildings, although cellular networks are now used in these areas, but signals Penetration has always been a shortcoming; the other is long-distance, battery-powered applications such as smart parking, asset tracking, and geological hydrological monitoring. Cellular networks can be applied but cannot solve high-power problems.
For enterprises deploying the Internet of Things, an important reason for choosing LPWA is the low cost of deployment. Everyone knows that the mainstream communication technology of smart home applications and intelligent hardware is WIFI. Because the module cost of WIFI is relatively low, some module providers with "Internet thinking" have reduced the price of WIFI modules to less than 10 yuan. However, IoT devices that support WIFI usually require wireless routers or wireless APs for network access, or only LAN communication. If you choose cellular communication technology, the deployment cost is too high for enterprises. The most common 2G communication module in China should start at 30RMB, while the 4G communication module should start at 200RMB. With the rise of the Internet of Things, although a bunch of manufacturers doing cellular communication modules have sprung up in China, the stability, plus the high power consumption and high cost of existing cellular communication technologies, is still worse than LPWA. Have an advantage. Huawei announced its NB-IOT development plan in November, claiming to reduce the cost of LPWA communication modules to less than $5. I believe that in the future low-power wide-area application scenarios, enterprises will still prefer LPWA.
Smd Led,Smd Fnd Display,Smd Led 0603 Display,Smd Led 0805 Display
Wuxi Ark Technology Electronic Co.,Ltd. , https://www.arkledcn.com