Softswitch technology and its application
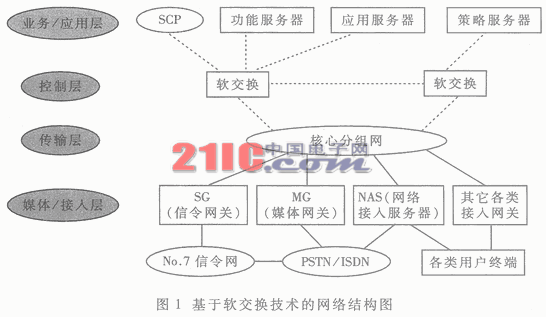
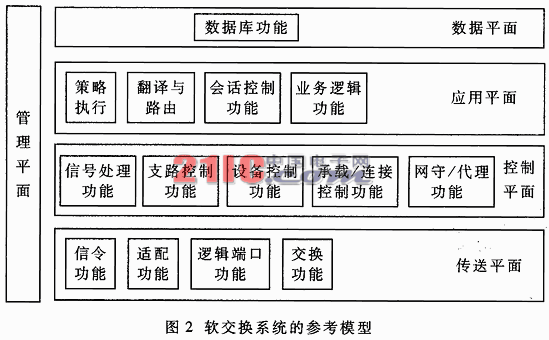
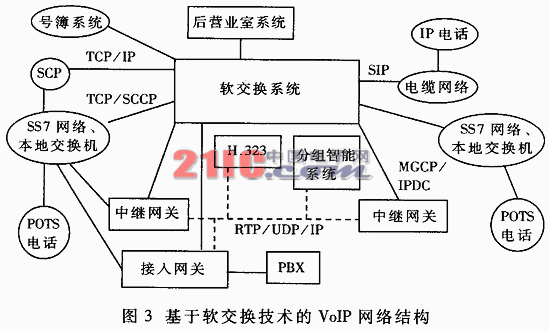
Abstract: Through the careful analysis of the basic principles of softswitch, the main features and functions of softswitch are discussed. The application of softswitch in VoIP is briefly introduced, and the problems that need to be studied in the development of softswitch are discussed. Keywords: softswitch protocol network principle application With the rapid development of communication network technology, people's requirements for broadband and services are also growing rapidly. In order to provide users with more flexible and diverse existing services and new services, and to provide users with more personalized services, The concept of a generation of networks, and currently major telecom operators have begun experimenting with next-generation communication networks. Softswitch technology is one of the focuses of next-generation communication network solutions, and has become a hot topic in the industry in recent years. China's Network and Switching Standards Research Group has completed the overall technical requirements framework for the softswitch system, and the 863 Program has also initiated research projects on softswitch systems in multimedia and mobile communication systems. 1 Proposal and definition of softswitch concept The concept of softswitch originated in the United States. At that time, in the enterprise network environment, the user implemented the PBX function (IP PBX) through a set of PC-based call control software (Call Manager, Call Server) using an Ethernet-based telephone. For such a set of equipment, the system does not need to lay the network separately, but only through the sharing with the local area network, the management and maintenance can be unified, and the comprehensive cost is much lower than the traditional PBX. Because the enterprise network environment has low requirements for reliability, billing, and management of devices, it is mainly used to meet communication requirements, and the device threshold is low. Many equipment vendors can provide such solutions. Therefore, IP PBX applications have achieved great success. Inspired by the success of IP PBX, in order to improve the overall operational efficiency of the network, the development of the network is more reasonable, open, and better serve the users. The industry has put forward such an idea: the traditional switching equipment is componentized and divided into call control and media processing. The standard protocol (MGCP, H248) is used between the two, and the software is mainly processed by pure software. Therefore, SoftSwitch (softswitch) ) Technology came into being. As soon as the concept of softswitch was proposed, it was quickly recognized and valued by the industry. The establishment of ISC (International SoftSwitch Consortium) accelerated the development of softswitch technology. The standards and protocols for softswitch were obtained by IETF, ITU-T, etc. The importance of the International Organization for Standardization. According to the definition of International Softswitch Forum ISC, Softswitch is a device and system that separates call control functions from media processing based on packet network using program control software. Therefore, the basic meaning of softswitch is to separate the call control function from the media gateway (transport layer), realize the basic call control function through software, and realize the separation of call transmission and call control, which is control, exchange and software programmable function. Establish a separate plane. Softswitch mainly provides functions such as connection control, translation and routing, gateway management, call control, bandwidth management, signaling, security, and call detail recording. At the same time, the softswitch also encapsulates network resources and network capabilities, and is connected to the service application layer through standard open service interfaces, so that new services can be quickly provided on the network. Softswitch is one of the core devices of the next generation network. When constructing a network structure based on softswitch technology, each operator must consider interworking with other various networks. In the next generation network, there should be a more unified network system structure. The network structure based on softswitch technology is shown in Figure 1. It can be seen from the figure that the softswitch is located at the network control layer, which better realizes the function of providing call control function and media processing separation based on the packet network using program control software. The interface between the softswitch and the application/service layer provides access to various databases, three-party application platforms, and function servers to support value-added services, management services, and three-party applications. The interface between the softswitch and the application server may use SIP, API, such as Parlay, to provide support for the three-party application and the value-added service; the interface between the softswitch and the policy server dynamically interferes with the work of the network device, and the COPS protocol may be adopted; The interface between the softswitch and the gateway center implements network management, adopts SNMP; the interface between the softswitch and the intelligent network SCP implements support for the existing intelligent network service, and adopts the INAP protocol. Through the interaction between the core packet network and the media layer gateway, the call related information in the process is received, and the gateway is instructed to complete the call. Its main task is to establish relationships between points, which can be simple calls or a more complex process. Softswitch technology is mainly used to process real-time services, such as voice services, video services, and multimedia services. The interface between the softswitches implements the interaction between the softswitch and the softswitch. SIP-T and H. 323 or BICC agreement. 3 The design principle of softswitch technology and its realization goal Softswitch technology is a distributed software system that provides seamless interoperability between networks based on a variety of different technologies, protocols, and devices. The basic design principle is to create a very scalable, interface. A distributed software system featuring standardization and business openness, which is independent of a specific underlying hardware/operating system and capable of handling the synchronous communication protocols required by various services, and is implemented in an ideal location. Push to the curve of the Moore curve. And it should be able to support the following basic requirements: (1) Calls independent of protocols and devices? Call processing of smoked devices and development of synchronous meeting management applications. (2) It is possible to securely execute a plurality of third party applications in its softswitch network without any harmful effects caused by malicious or misbehaving applications. (4) Business and application providers can increase their ability to support system-wide policies without compromising performance and security. (5) Ability to perform synchronous communication control to support a variety of post-office systems including billing, network management, and other operational support systems. (6) Dynamic topology of a synchronous communication control network that supports runtime bundling or contributes to structural improvement. (7) Small to large network scalability and support for complete fault recovery. The goal of softswitch is to realize protocol conversion of various media streams through computer software programming in cooperation with media devices and media gateways, and implement IP network and ATM network based on packet network (IP/ATM) architecture. Interconnections such as PSTN networks provide devices that have the same functions as circuit switches and are convenient for service value addition and flexibility. The reference model of the softswitch system is shown in Figure 2. 4 The main protocol used by the softswitch The softswitch system involves a lot of protocols, including H. 248, SCTP, ISUP, TUP, INAP, H. 323, RADIUS, SNMP, SIP, M3UA, MGCP, BICC, PRI, BRI, etc. Internationally, IETF, ITU-T, SoftSwitch Org and other organizations have played an active leading role in the research of softswitches and protocols. Many key protocols have been formulated or completed. These agreements will standardize the research and development of the entire softswitch, so that the product will enter the stage of using the industry's common standard protocol from the use of the private agreement phase of each manufacturer, and the interoperability between products will become possible. The original intention of softswitch generation is to provide a standard. With an open system architecture, each network component can be developed independently. In terms of the research progress of softswitch, China is at the level of world synchronization. The “Network and Exchange Standards Research Group†of the Ministry of Information Industry initiated research on softswitch projects in the second half of 1999, and has now completed the “General Technical Requirements for Softswitch Equipmentâ€. In addition, the "IP Standards Research Group" is developing technical specifications for equipment such as relay media gateway (TG), signaling gateway, SG snow, access gateway (AG), integrated access equipment, and IAD snow. Here is a brief introduction to several major protocols. 1. H. 248/MEGACO H. Both the 248 and MEGACO protocols are referred to as Media Gateway Control Protocols, applied to the Media Gateway and H. Between 248/MEGACO and softswitch equipment. The contents of the two agreements are basically the same, just H. 248 was proposed by the ITU, and MEGACO was proposed by IEFT and is a joint recommendation between the two parties. They introduce two abstract concepts of Termination and Context. In the Termination, the parameters of the media stream, the MODEM and the bearer capability parameters are encapsulated, and the Context indicates the interconnection relationship between some Terminations. H. 248/MEGACO completes the operation between the Termination and the Context through 8 commands such as Add, Modify, Subtract, and Move, thus completing the establishment and release of the call. 2. Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) The Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) was proposed by IEFT and is a combination of Simple Gateway Control Protocol (SGCP) and IP Device Control Protocol (IPDC). The MEGACO protocol is a further improvement, improvement and improvement of the MGCP protocol. The MGCP protocol can be said to be a relatively mature protocol. The content of the protocol is similar to the MEGACO protocol. At present, most of the softswitch system equipment supports this protocol, and its shortcomings are slowly manifested. It may be H. Replaced by the 248/MEGACO agreement. In the softswitch system, MGCP protocol and H. Like the 248/MEGACO protocol, it is applied between the media gateway and the MGCP terminal and the softswitch device. This protocol controls the connection, establishment and release of the media/control flow on the media gateway and the MGCP terminal. 3. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an application layer control protocol proposed by the IETF for multimedia communication over an IP network. Based on the Internet Protocol (HTTP), it follows the design principles of the Internet and is based on the peer-to-peer mode of operation. Sessions can be connected, established, and released using SIP, and support for unicast, multicast, and mobility. In addition, if used in conjunction with SDP, SIP can dynamically adjust and modify session attributes such as call bandwidth, transmitted media type, and codec format. See IETF RFC 2543bis for details. In the softswitch system, the SIP protocol is mainly applied between the softswitch and the SIP terminal, and some manufacturers apply the SIP protocol between the softswitch and the application server to provide value-added services based on the SIP protocol. In general, the SIP protocol is mainly applied to the combination of voice and data, and call setup and release between multimedia services. In particular, the SIP protocol, with its simple and flexible features, has made 3GPP, which is a mobile communication standardization organization, have decided to establish an all-IP network for third-generation mobile communications on its basis, and requires that future 3G terminals must support the SIP protocol. 4. SCTP protocol The SCTP protocol is a flow control transfer protocol proposed by the IETF. Primarily, PSTN signaling information is transmitted over a connectionless network, which provides reliable data transmission over an IP network. In the acknowledgment mode, SCTP can transmit user data without error and without repetition, and segment user data according to the MTU limitation of the path; ensure the sequential delivery of user messages on multiple streams, and message multiple users Copy to the data block of SCTP. The SCTP coupling mechanism is used to ensure partial fault self-processing at the network level. SCTP also features congestion avoidance and avoidance of flooding and anonymous attacks. The SCTP protocol plays the role of the primary bearer of the control protocol in the softswitch. 5 Main features and functions of softswitch technology 1. The main features of softswitch technology are reflected in the following aspects: (1) A programmable call processing system supporting various networks such as various PSTN, ATM, and IP protocols. (2) It can be easily run on various commercial computers and operating systems. (3) Efficient and flexible. E.g: Softswitch plus a trunking gateway is an alternative to a long-haul/tap switch (C4 switch) with VoIP or VTOA functionality in the backbone. Softswitch plus an access gateway is an alternative to a voice virtual private network (VPN)/private branch exchange (PBX) trunk with VoIP capabilities in the backbone. Softswitch plus a RAS can utilize the public bearer relay to provide managed MODEM services. Softswitch plus a trunking gateway and a local performance server are an alternative to a local switch (C5 switch) with VoIP or VTOA functionality in the backbone. (4) Openness The IN (Intelligent Network) service can be reused through an open and flexible directory interface. For example, it provides a directory embedding mechanism with access to a relational database management system, a lightweight directory access protocol, and a transaction capability application partial directory. (5) Provide an open application programming interface (API) for third-party developers to create next-generation services. (6) With programmable post-office features. For example: programmable event detail records, detailed call events are written to a service provider's collection event device. (7) Features advanced policy server-based management of all software components. Includes a simple network management protocol interface exposed to all components, a policy description language, and a system for writing and executing customer policies. 2. Softswitch is a collection of multiple logical functional entities. It provides call control, connection and partial service functions for integrated services. It is the core device for voice, data and video service call, control and service provision of next-generation telecommunication networks. The main functions are as follows: (1) Call control and processing provide control functions for the establishment, maintenance, and release of basic calls. (2) The protocol function supports the corresponding standard protocol, including H. 248, SCTP, H. 323, SNMP, SIP, etc. (3) The service provision function can provide various general or personalized services. (4) Service switching function (5) The interworking function can realize interworking with the response device through various gateways. (6) The resource management function centrally manages various resources in the system, such as resource allocation, release, and control. (7) The billing function transmits the bill to the billing center according to the operational requirements. (8) The authentication/authorization function can perform authentication and authorization to prevent unauthorized users or devices from accessing. (9) Address resolution function and voice processing function. With the continuous development of communication network technology and the formulation and supplement of various standards for softswitch, many manufacturers have introduced softswitch solutions, and operators are actively conducting related experiments. At present, many telecom equipment manufacturers at home and abroad, such as Siemens, Alcatel, Ericsson, Nortel, and ZTE, are actively developing new switch transition platforms and propose solutions for softswitch in next-generation networks. Here is a brief introduction to the application of softswitch in VoIP. Figure 3 shows the structure of VoIP network based on softswitch technology. As can be seen from the figure, its function is very similar to the switching/long-distance network between the current circuit-switched transmission systems, and the C4 switch is replaced by a combination of a softswitch system and a group of trunking gateways. The trunking gateway itself is controlled by the softswitch technology using the master/called protocol, which is the MGCP/IPDC protocol associated with a specified time slot from a circuit switch with a specified source/destination RTP/UDP/IP flow. . As part of the call processing, the softswitch technology identifies the most likely egress gateway to be used to terminate the call and uses this information to command the trunking gateway to perform the specified functions, ie the softswitch technology can be selected A minimum cost route is used to complete each call so that the selected egress gateway is closest to the destination phone. Thus, the call operation function originally performed through the circuit switched network is completed. The access gateway can either terminate the ISDN PRI or terminate the CAS signaling from the enterprise PBX. Such access gateways can be controlled by softswitches in a variety of ways based on packet telephony protocols; for H. based The gateway of the 323 protocol, the softswitch can be like an H. The 323 gateway acts like this; if the access gateway tunnel PRI (Q.931) or CAS signaling returns to the softswitch, the softswitch can also use a MGCP/IPDC protocol to control the access gateway in a better way. This also reflects the ability of softswitch technology to handle access gateways. Softswitch technology is connected to the cable network via the SIP protocol to support enterprise IP PBX and IP telephony. It can also access the SCP via the TCP/IP protocol, or it can be connected to the SS7 network via the TCP/SCCP protocol, making seamless interconnection possible. 7 Major issues that need to continue to be addressed in next-generation networks based on softswitches Although the next-generation network based on softswitch is a relatively complete network solution, it can be applied in various communication fields. However, due to its new technology, most of the current solutions are in the experimental stage, and large-scale applications have not yet been formed. Many problems still need to be solved. Continue to pay attention to issues such as QOS, gateway, security, service delivery methods, and organic integration with existing networks. 1. QOS problem QOS guarantees are a very important issue for any network. Fundamentally speaking, the softswitch itself does not solve the QOS problem, but relies on its bearer network to guarantee the quality of service. There are currently two ways to host a network: ATM and IP. For the bearer network of ATM, it has a strong QOS mechanism. However, for the IP bearer network, how to solve the QOS problem. In the next-generation network based on softswitch is a very critical issue, because from the current situation of equipment development and the general trend of network development, IP as the bearer network should be the general trend. 2. Softswitch network management From the current implementation of softswitch, most of them use SNMP as the network management protocol of the softswitch system, but the SNMP network management system has certain limitations. The SNMP network management is mainly based on static management and cannot be used for various services. Comprehensive management of demand changes. Because SNMP uses a UDP-based bearer, the reliable transmission of network management information cannot be guaranteed. At the same time, the next-generation network based on softswitch provides real-time services, and the network management system must have certain QOS management capabilities. However, the current network management system based on softswitch has relatively poor ability to handle this aspect, and further improvement and improvement are needed to meet the requirements of users for service quality. 3. The protocol involved in softswitch still needs to be improved Open communication protocols are used between the various network interfaces of the softswitch network. However, at present, whether from the formulation of the agreement or the development of various manufacturers, the standardization of the interface is still not perfect, and most of the agreements are still in the stage of expansion and improvement. Therefore, it will take some time from the final open network. In summary, although soft exchange has great development potential, it is still in the initial stage of development. The communication system with softswitch as the core will provide business opening capability, conform to the development trend of triple play, provide voice, data, video services and multimedia converged services to meet the communication personalized, mobile and access to information anytime, anywhere. aims. |
Karaoke Speaker,Karaoke Speakers,Karaoke Speakers For Sale,Karaoke Speakers Bose
gdfhdfhdhs , http://www.nbspeakers.com