468 mechanical engineers must know the mechanical common sense, collection!
1. The main forms of metal structures are: frame structure, container structure, box structure, and general component structure.
2. The riveting operation can be divided into: preparation, layout, processing and assembly, and assembly and connection according to the nature of the process.
3. The connection methods of metal structures include: riveting, welding, rivet welding, and bolting.
4. Riveting in the mechanical manufacturing industry is classified as a thermal processing category.
5. Thermal processing involves heating all or part of the metal material to form it.
6. A truss structure is made using (profiles).
7. The structure of the container is a structure made primarily from (plates).
8. The structure of the box and the general structure are made from a combination of (sheets) and (profiles).
9. Preparation refers to the preparation of (raw materials) and (part blanks).
10. Steel plates and profiles can deform during transportation (suspension, storage, and storage).
11. Deformation of steel will affect the normal operation of parts (lifting, unloading, gas cutting).
12. If deformation of parts during processing is not corrected, it will affect the correct assembly of the structure.
13. Deformation caused by welding reduces the assembly (accuracy), causing additional stress inside the steel structure, affecting (member strength).
14. Deformation of flat steel includes: bending, twisting, and combined bending and twisting deformation.
15. Multi-roller straightening machines can be divided into upper and lower roller row parallel straightening machines and upper and lower roller tilt straightening machines based on the arrangement of the shaft rollers and the position of the adjusting roller. (Source: Metal Processing)
16. Flame correction heating methods include: point, line, and triangle heating.
17. The effect of flame correction is determined by (heating position and temperature).
18. Corrective methods include: mechanical correction, manual correction, flame correction, and high-frequency heat reaming.
19. Layout and numbering are the first steps in making metal structures.
20. Layout and numbering directly impact product quality, production cycle, and cost.
21. Commonly used quantities for layout include: wooden folding ruler, ruler, steel tape measure, and steel ruler.
22. Commonly used tools for layout include: rule, ground gauge, sample punch, needle, and small hand hammer.
23. The procedure for real-time layout is: linear layout, structural layout, and opening.
24. The contents of the exhibition sample include: plate thickness processing, unfolding drawing, and making a sample material.
25. Samples are divided according to their use: sample material samples, inspection sample plates, and positioning templates.
26. The prototype is generally made of thin iron sheets with a thickness of 0.5-2 mm.
27. The drawing methods of the sample and sample rods mainly include: straight line drawing method and transitional drawing method.
28. How to make reasonable material usage?
A: It is necessary to concentrate on the use of spares and surplus materials.
29. Curves are divided into plane curves and space curves.
30. The method for calculating the length of a straight segment is: rotation method, right triangle method, branch line method, and face changing method.
31. The procedure for the open sample is to draw the intersecting line, the solid long line, the solid shape, and then make the unfolded picture by geometric drawing.
32. The basic methods for finding a plane intersection line are: ridge method and facet method.
33. The basic methods for finding the three-dimensional intersection line are: warp method and weft method.
34. The main methods for finding the intersection line are: the auxiliary plane method, the plain line method, and the spherical method.
35. What are the characteristics of the intersection line?
Answer: (1) The intersection line is the common line and dividing line of the two intersecting shapes. (2) Since the shape has a certain range, the intersection line is always closed.
36. Intersection line: the intersection of the section plane and the solid surface.
37. Prime line: any position on the surface of the component is called the prime line.
38. Commonly used expansion methods are: parallel line method, radiation method, and triangle method.
39. The division of the spherical surface usually includes: the banding method, the blocking method, and the splitting method.
40. The main content of the thickness treatment is to determine the neutral layer of the curved part and eliminate the thickness interference.
41. The length of the angle steel bending piece is calculated as (center of gravity).
42. Shearing machines for cutting straight lines include: gantry oblique shearing machines, cross-beam oblique shearing machines, and combined punching and shearing machines.
43. The cutting curve of the machine tools include: disc shears, vibratory shears.
44. What are the characteristics of the vibration shearing machine?
A: Vibration shears can cut a variety of curves and bores.
45. The combined shearing machine consists of (oblique shears, steel shears, small punches).
46. Try to analyze the transmission sequence of the shearing machine: the original moving part → the transmission part → the workpiece.
47. The front and rear baffles of the gantry shears have: positioning.
48. On the gantry or oblique mouth shearing bed, the positioning shearing is: shearing plate positioning shearing, tailgate positioning shearing, baffle positioning shearing.
49. The shear force acting on the material by the oblique shear can be decomposed into: shear force, horizontal tension, and exit force.
50. Shearing machinery: Not suitable for shearing alloy materials and quenched materials.
51. The cutting oxygen pressure is selected according to the thickness of the workpiece, the torch nozzle aperture, and the oxygen purity.
52. The ignition point of general carbon steel in oxygen is: 1100-1150 °C.
53. Metal materials that can meet the gas cutting conditions are: pure iron, low carbon steel, medium carbon steel, ordinary low alloy steel.
54. The process of gas cutting is: preheating of metal, burning of metal, and blowing of oxides.
55. What is the role of a circular die? What is the composition?
A: It is a tool for machining external threads, which consists of a cutting part, a positioning part, and a chip removal hole.
56. What is the form of the sloping groove?
A: The type and thickness of the material, the welding method, and the mechanical properties of the product.
57. Scrub: The machining of the surface of a workpiece with a grinding wheel is called sanding.
58. Grinding tools mainly include: pneumatic grinders and electric grinders.
59. What is the deformation of the steel during the bending process?
A: Elastic deformation and plastic deformation will occur.
60. Commonly used bending methods for riveting include: cold bending, hot bending, manual bending, and mechanical bending.
61. The material is bent and deformed during press forming: free bending, contact bending, and correcting bending.
62. The variation of the cross-sectional shape of the material during bending is related to the relative bending radius, the geometry of the cross-section, and the way of bending.
63. The method of preventing the offset of the blank during bending is: having a feeding device and positioning holes.
64. Rolling machines include: roller machines and section bending machines.
65. The main processes of manual bending are: scribing, sand filling, heating and bending.
66. Metal structure joint methods are: rivet joint, threaded joint welding three.
67. Select the connection method to consider: the strength of the component, the working environment, materials, construction conditions and other factors.
68. Riveted joints are available in: butt joints and corner joints.
69. Solid rivet heads are available in the form of semi-circular heads, countersunk heads, and semi-sunk heads.
70. AC arc welders are mainly BX1--330 and BX--500.
71. The basic operation process of hot riveting is: fastening by riveting, repairing holes, heating of rivets, nailing and nailing, top nailing, riveting.
72. The types of riveting are: strong riveting, dense riveting, and tight riveting.
73. Tools for hole repair are: reamer.
74. Commonly used anti-loose measures for threaded joints are: increased friction and mechanical anti-loose.
75. The welding arc consists of an anode zone, a cathode zone and an arc column.
76. Electric welders mainly include: DC welders and AC welders.
77. Local deformation: refers to the deformation of a part of the component, including angular deformation, wave deformation, local unevenness.
78. Welding is divided into space positions: flat welding, vertical welding, horizontal welding, and overhead welding.
79. In which direction does the electrode move in the welding process?
Answer: It moves in the direction of the molten pool, moves in the welding direction, and oscillates in the lateral direction.
80. The three elements of assembly are: positioning, support and clamping.
81. Manual clamps include: screw clamps, wedge clamps, lever clamps, and eccentric clamps.
82. Non-manual clamps have: pneumatic clamps, hydraulic clamps, and magnetic clamps.
83. The screw clamp has the functions of clamping, pressing, topping and supporting.
84. Commonly used measurement items in assembly are: linear size, parallelism, verticality, coaxiality, and angle.
85. The form of support of the workpiece in the assembly is: assembly platform support, assembly of the frame support.
86. Assembling the tire frame can be divided into: a universal tire frame and a special tire frame according to its function.
87. The positioning methods commonly used in assembly are: scribing positioning, template positioning, positioning component positioning.
88. The basic methods for finding the plane intersection line are: facet method and ridge line method.
89. Hot rivet is generally composed of four people. What is their division of labor?
A: One person heats and transfers, one nails nails, one nails, and one person rives.
90. What is the role of the flat tail in a taper bit?
A: It is used to increase the transmitted torque and avoid the drill bit being punched in the spindle hole or drill sleeve.
91. What is the role of the guiding part in the drill bit?
A: It keeps the drilling direction of the bit straight during the cutting process. At the same time, it has the function of repairing the wall of the hole and is also a backup part of the cutting portion.
92. What are the undesirable phenomena when the hole is about to be drilled?
Answer: When the drill bit just drills through the workpiece, the axial resistance suddenly decreases. Due to the sudden recovery of the gap and elastic deformation of the drilling machine, the drill bit will be automatically cut at a large feed rate, resulting in the fracture of the drill or the quality of the drill. reduce.
93. What is the role of cutting fluid in drilling?
A: Reduce friction, reduce bit resistance and cutting temperature, improve the cutting ability of the drill bit and the surface quality of the hole wall.
94. Cutting amount: It is the general term for cutting speed feed and cutting depth.
95. Grinding: It is the method of machining the surface of the workpiece with a grinding wheel.
96. Unfolding: The process of spreading the surface or part of a metal structure in a plane according to its actual shape size is called unfolding.
97. The methods for drawing out the map are: parallel line method, triangle method, and radiation method.
98. The condition of the parallel line method is that the plain lines on the surface of the member are parallel to each other and reflect the real length on the projection surface.
99. Sheet thickness processing includes: determining the neutral layer of the curved member and eliminating plate thickness interference.
100. The change in the position of the plate thickness neutral layer is related to the bending radius of the plate and the thickness of the sheet.
101. The general principle of the thickness of the intersecting part is that the unfolded length is based on the size of the neutral layer of the member, and the height of the curve in the unfolded view is based on the height of the contact of the member.
102. The main contents of the stakeout are: plate thickness processing, unfolding the drawing, and making a sample material based on the developed component drawing.
103. Commonly used shearing equipment for rivets include: gantry shearing machine, oblique shearing machine, disc shearing machine, punching shearing machine combined punching and shearing machine.
104. The bending machine can be divided into three types: symmetrical three-roller, asymmetric three-roller and four-roller according to the number and arrangement of the shaft rollers.
105. Punching die can be divided into simple mold, guided column mold and composite mold according to structure.
106. The structural feature of the composite blanking die is that it has a convex and concave die which acts both as a blanking punch and a punching die. (Source: Metal Processing)
107. Punching force: refers to the maximum resistance of the material to the mold during blanking.
108. The deformation process of sheet separation during blanking can be divided into: elastic deformation stage, plastic deformation stage and shear stage.
109. Minimum bend radius: The minimum bend radius that can be achieved without damage to the material.
110. Common methods for reducing the rebound of the bending parts are: correction of the mold method and pressure correction method.
111. The purpose of the crimping ring when stretching is to prevent wrinkling of the edges of the tensile member.
112. What is the role of the crank-link mechanism of the crank press?
A: It not only makes the rotary motion into a reciprocating linear motion, but also amplifying the force.
113. Sheet metal hand forming includes: bending, arching, burring, crimping, seaming and correction.
114. Exhibit samples can be used for: numbering, manufacturing separate molds and manufacturing milled samples.
115. Releasing: The operation of stretching and thinning the edge material of the deformed part during the forming process is called edging. The formation method is thinning and thinning.
116. Pulling the edge: Using the edge and edge method, the edge of the sheet is processed into a curved curved workpiece.
117. Crimping: The edge of the workpiece is curled to increase the rigidity and strength of the edge of the workpiece.
118. Bite: The edges of two sheets or the sides of a sheet of material are folded and bitten together and pressed together, called a bite.
119. Thickness treatment: The method taken to eliminate the influence of the thickness of the sheet on the shape and size of the developed image.
120. The general procedure for calculating the unfolded length of a curved member is to divide the curved member into straight segments and arc segments; calculate the length of each segment separately; add the calculated lengths.
121. Under what circumstances is the application of steel incision blanking?
Answer: Angle steel, channel steel and I-beam are bent into a corner.
122. The entire blanking process is divided into: elastic deformation stage; plastic deformation stage; shear stage.
123. Punching: A stamping process in which a stencil is used to separate a portion of a sheet from another portion along a certain closed line.
124. Bolted joints: There are two types: joints that are subjected to axial tensile load; joints that are subjected to lateral action.
125. The anti-loose measures for bolted joints include: increased friction; mechanical anti-loose.
126. Mechanical anti-loose: split pin; retaining washer; retaining washer; tandem wire.
127. Welding arc: A strong and long-lasting discharge occurs in the gaseous medium between the two electrodes.
128. The welding arc consists of: the cathode region; the anode region and the arc column.
129. Which three directions of movement do the electrodes have?
Answer: Move toward the molten pool; move in the welding direction; swing horizontally.
130. Welds can be divided into: flat welding, vertical welding, horizontal welding and overhead welding according to their spatial position.
131. What are the characteristics of the intersecting line?
A: The public cable is also the dividing line on the surface of the two shapes; the space is always closed.
132. Intersecting line: A member consisting of two or more geometric intersections.
133. The factors affecting the quality of the blanking are: the mold gap; the center line of the convex and concave molds do not coincide; the working edge of the mold becomes dull.
134. The general principle of mold design is: strive to design the mold under the premise of ensuring the quality of stamping, easy to manufacture, simple and low cost, easy to use.
135. The purpose of calculating the calendering force is to select the calendering equipment correctly.
136. Free bending: When the bending is finished, the punch, blank and die will not interfere with each other.
137. Correction of bending: refers to the punch, blank, and die. After the three are matched, there is also an impact, which corrects the curved part.
138. What are the defects that are easy to produce when sealing the head? (Source: Metal Processing)
Answer: wrinkle and bag; straight edge pull pit; outer surface microcrack; longitudinal tear; skew; ellipse;
139. Expansion joint: The joints of the pipe and the tube sheet are deformed to achieve sealing and fastening.
140. The purpose of calculating the punching force is to rationally select equipment capabilities and design molds.
141. What methods can be used to reduce the punching power?
Answer: oblique blade die; step die; heating die.
142. The purpose of calculating the bending force is to select a curved press and design a mold.
143. What is the extent of the deformation?
A: The degree of sticking; the extent to which the material pull allows deformation.
144. How to determine the number of pulls of the workpiece?
A: According to the maximum deformation of the workpiece being pulled and the elongation of the material.
145. How is the pull factor determined?
A: Depends on the properties of the material, the wrap angle, the coefficient of friction and whether it is prefabricated.
146. Brittle materials such as high carbon steel, high alloy steel and cast iron are not suitable for cold work.
147. When the angle steel is in complex deformation, its order of refinement is: first correct the distortion, then correct the bending and correct the angular deformation.
148. Causes of deformation of the steel structure: one is caused by external force and the other is caused by internal stress.
149. Methods for eliminating welding residual stress include: overall high temperature tempering; local high temperature tempering; temperature difference stretching method; mechanical stretching method;
150. Overall deformation of welding: refers to the change in shape and size of the entire structure.
151. Hammering method: The fiber structure of the metal sheet is elongated by hammering.
152. Rivet rod length: determined according to the total thickness of the connected parts, the gap between the nail hole and the shank diameter, the riveting process and other factors.
153. The reason why the rivet head is too small after riveting is that the shank is short or the hole diameter is too large.
154. When welding, according to the state of the metal, it can be divided into: welding, pressure welding, brazing.
155. Fusion welding: A method of using localized heating to bring the welded joint into a molten state.
156. Clamping: The external force is used to fix the positioned parts so that they remain in position during machining.
157. Six-point positioning rule: Six anchor points are used to limit the freedom of the part in space to determine the spatial position of the part.
158. Relative Parallelism: Refers to the parallelism of the line or face being measured on the part relative to the measurement reference line or face.
159. Relative perpendicularity: refers to the vertical extent of the line or face being measured on the part relative to the measured reference line or face.
160. The work clamps used in the assembly are: assembly tools; assembly fixtures; assembly spreaders.
161. Commonly used assembly cranes are: wire rope, iron chain, chain hoist and special spreader.
162. How many forms of guidance are there for punching?
A: There are two types of guide posts, guide bushes and guide plates.
163. How many parts does the punching die have?
Answer: It consists of the working part, the material positioning part, the unloading part and the mold base.
164. What is the role of the tensile die gap?
A: Reduce the friction between the material and the die and control the flow of material in the cavity of the die.
165. According to its structure, the bite seam can be divided into: vertical single bite seam; vertical double bite seam; horizontal flat bite seam and various corner bite seams.
166. What is the cause of the rebound of the bent piece when the external force is removed?
A: Because the outer surface of the sheet is pressed by the inner surface of the sheet when it is bent by hand, it rebounds.
167. The cold arch is obtained by shrinking the edge of the sheet to the middle of the sheet, and the heat arch is obtained by shrinking the sheet by heating. (Source: Metal Processing)
168. There are two ways to pull the edge. One is to use a universal tool to pull the edge, and the other is to use a type of tire to pull the edge.
169. Edge: The edge is first wrinkled, and then the wrinkles are flattened to prevent the stretch from recovering. Thus, the length of the sheet is reduced and the thickness is increased.
170. The basic principle of the edge is that the forming of the workpiece with the convex curve is mainly due to the shrinkage of the outer edge material of the curved plane edge, which is thickened and shortened, forcing the vertical edge to have a curved shape.
171. The purpose of the correction is to shorten the longer fibers and to lengthen the shorter fibers by applying external force or local heating, and finally to make the fibers of the layers uniform for the purpose of correction.
172. The principle of flame correction is to use the deformation caused by local heating of the metal to offset the original deformation and achieve the purpose of correction.
173. Factors affecting the flame correction effect are: rigidity of the workpiece; heating position; heat of the flame; heating area and cooling method.
174. Flame correction is heated in the form of dots, lines and triangles.
175. The factors determining the process margin are: the influence of the stakeout error; the influence of the error during the machining of the part; the influence of the assembly error; the influence of the welding deformation; the influence of the flame correction.
176. Samples can be divided into: sample materials, molding samples, positioning templates and sample rods according to their uses.
177. The drawing methods are: direct drawing method and transition drawing method.
178. How do you choose the stakeout baseline?
Answer: Take two lines or faces that are perpendicular to each other; use two center lines as the reference line; base on one plane and one center line.
179. Stakeout allowable error: During the process of stakeout, due to factors such as stakeout gauge and tool accuracy and operation level, the sample plot will have a certain dimensional deviation. If the deviation is controlled within a certain range, it is called stakeout. error.
180. Structural staking includes: determining the joint position and connection form of each part; giving necessary changes according to the actual production and processing capacity; calculating or measuring the actual length of the part material and the plane parts; designing the tire or the tire frame.
181. The method for finding the real length of a straight line segment is: rotation method; right triangle method; face changing method; branch line method.
182. What is the rule of drawing for the real length of a line segment by a right triangle method?
A: The projection of the line segment on any projection surface is used as a right angle side of the right triangle, and the projection length on the axis perpendicular to the plane is used as the other right angle side, and the oblique side is the real length of the line segment.
183. Rotation method to find the real length: just rotate the general position of the space around a fixed axis into a parallel line, then the projection of the line on the projection plane parallel to it reflects the real length.
184. The methods for finding the actual length of the curve are: face-changing method; expansion method.
185. Face changing method: another new projection surface is parallel to the curve, and the projection of the curve on the surface reflects the real length.
186. Expansion method: the expansion line that straightens one length in the curve view while keeping the height in the other view unchanged.
187. The basic feature of the intercepting line is that the intersecting line must be a plane figure enclosed by a closed line or curve; the intersecting line is a common line between the sectional plane and the solid surface, which is made up of both on the sectional plane. It is also a collection of points on the three-dimensional surface.
188. Methods for finding three-dimensional intercept lines are: facet method; ridge method.
189. The methods for finding the three-dimensional intersection line of the curved surface are: the plain line method and the weft method.
190. What are the characteristics of the intersecting line?
Answer: First, the common line intersecting the surface of the two shapes is also the dividing line of the intersecting two shapes; the second is that the intersecting lines are closed.
191. The essence of the intersecting line is to find a certain number of common points on the surface of the two shapes, and to connect these common points in turn.
192. The selection principle of the method of finding the intersecting line is: using the prime line method to find a projection of the intersecting line at least the known intersecting line; using the auxiliary plane method to find the intersecting line, the intersecting line should be the simplest geometric figure. The spherical method is only applicable to members where the rotating bodies intersect and the axes intersect.
193. Under what conditions, the intersecting line is a plane curve? The front projection of the curve is the intersection of two straight lines?
Answer: When two rotating bodies circumscribed by the same spherical surface intersect, the intersecting line is a plane curve. At this time, when the axes of the two rotating bodies are parallel to the basic projection surface, the intersecting line is on the surface. The projection is the intersection of two lines,
194: Straight surface: It is a surface formed by a straight line as a bus.
195: What are the characteristics of the cylinder?
Answer: All the prime lines are parallel to each other; when the cylinders are cut by planes parallel to each other, the section patterns are the same.
196: What are the characteristics of the cone?
Answer: All the prime lines intersect at one point; when the tapered surfaces are cut by planes parallel to each other, the cross-section patterns are similar; the intersecting lines at the top of the cone are triangular.
197: When drawing, the plastic deformation process of the material is divided into: the material is bent; the material is stretched and deformed;
198: Pulling shape: It is the forming method that the sheet material is plastically deformed according to the ideal curved surface under the tension state and overcomes the rebounding. (Source: Metal Processing)
199. Sheet thickness processing includes determining the neutral layer of the curved member and eliminating plate thickness interference.
200. The change in the position of the plate thickness neutral layer is related to the bending radius of the sheet and the thickness of the sheet.
201. The general principle of the thickness of the intersecting part is that the unfolded length is based on the size of the neutral layer of the member, and the height of the curve in the unfolded view is based on the height of the contact of the member.
202. The main contents of the stakeout are: plate thickness processing, unfolding the drawing, and making a sample of the material based on the developed component drawing.
203. Commonly used shearing equipment for rivet workers are: gantry shearing machine, oblique shearing machine, disc shearing machine, punching shearing machine combined punching and shearing machine.
204. The bending machine can be divided into three types: symmetrical three-roller, asymmetric three-roller and four-roller according to the number and arrangement of the shaft rollers.
205. Punching die can be divided into simple mold, guided column mold and composite mold according to structure.
206. The structural feature of the composite blanking die is that it has a convex and concave die which acts as both a blanking punch and a punching die.
207. Punching force: refers to the maximum resistance of the material to the mold during blanking.
208. Rebound: In the bending process, when the external force is removed, the recovery phenomenon of the material due to elasticity is called rebound.
209. Stretching: A stamping process for forming sheets into open hollow parts using a press and corresponding mold.
210. Tensile coefficient: The ratio of the cross-sectional area of the material after each stretch to the end area before stretching is called the stretch factor of the time. The stretch factor actually reflects the degree of deformation of the tensile member.
211. Blanking ring: In the process of stretching, in order to prevent wrinkling of the edge of the workpiece, wrinkles are formed, and a ring-shaped pressing device is provided at the edge portion between the concave and the convex die.
212. The working principle of the friction press is to use the contact drive of the flywheel and the friction disc and work with the principle of relative movement of the screw and the nut.
213. What are the advantages of friction presses?
A: The action is faster, so that the slider can be stopped at any position within the stroke. Once overloaded, only the sliding between the flywheel and the friction disc is caused, and the mechanism is not damaged.
214. What are the advantages of the stamping process?
Answer: (1) High production efficiency. One stroke of the press can complete one process, and sometimes multiple processes can be completed. (2) High material utilization rate. (3) The stamping parts of the same product have the same shape and size and good interchangeability. (4) Simple operation, easy to realize mechanization and automated production.
215. Stamping process: separation process, molding process, and compound process.
216. Punching: A stamping method that uses a die to separate the sheets on a press.
217. How to distinguish between punching and blanking?
A: Under normal circumstances, the sheet is punched to form two parts, namely the flushing part and the holed part. If the purpose of the punching is to obtain a workpiece of a certain shape, that is, the flushing part is called a blanking material: the purpose of punching is to machine a certain shape of the inner hole, and the flushing is a waste material, which is called punching.
218. What are the stages in the separation process of materials when punching?
A: elastic deformation, plastic deformation, crack separation.
219. The methods for reducing the punching force include: oblique edge punching, stepped punch punching, and blank heating punching.
220. Minimum Bending Radius: The minimum limit of the bending radius when the material is bent and does not cause damage, called the minimum bending radius.
221. External forces that cause deformation of structural members include: bending force, torsion, impact force, tension, pressure, and the like.
222. What can external forces cause inside the component? When the external force is removed, some internal forces may be retained. What does it form?
Answer: External force can cause internal force inside the component: When the external force is removed, internal stress is formed.
223. What is the process and the process of the welding process for metal structural parts? What is the main cause of deformation caused by components?
A: It is an uneven heating and cooling process: it is the main cause of deformation caused by internal stress of the component.
224. What are the major constrictions in the welds and the shrinkage of the metal near the weld?
A: Mainly in the contraction of the longitudinal and horizontal directions.
225. The factors that may cause structural deformation in the design are: the rationality of the structure, the location of the
10KW-200KW Three-Phase Inverter
10KW-200KW Three-Phase Inverter
CHARACTERISTIC
â—Online working mode design, high speed static switching..Superior load characteristics
â—Perfect protection function
â—High performance dynamic characteristicselntelligent battery management
â—Optional battery patrol module
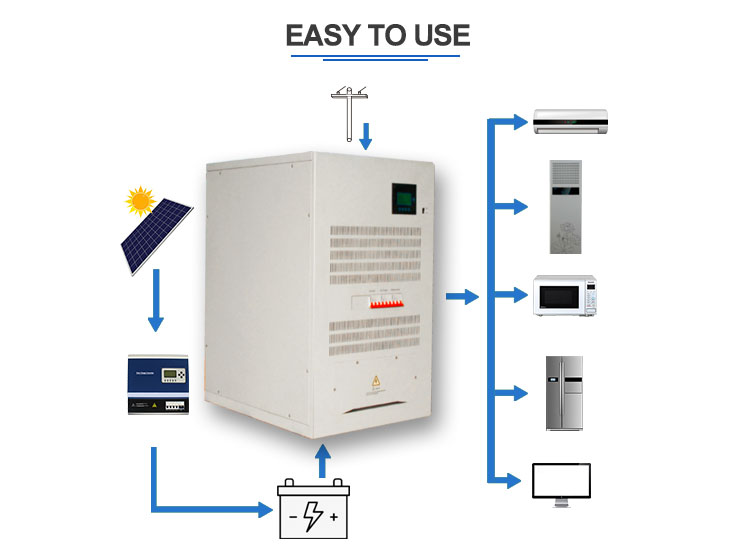

Nkm Hybrid Inverter With Mppt Charge,Inverter Power Inverter,Hybrid Inverter Charger,Hybrid Grid Tie Inverter
suzhou whaylan new energy technology co., ltd , https://www.xinlingvideo.com